NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity In this article, we will provide you all the necessary information regarding NCERT solutions for class 10 science physics chapter 12 electricityWorking on CBSE class 10 physics electricity questions and answers will help candidates to score good marks inclass tests as well as in the CBSE Class 10 board examOhm (Ω) Ohm is the electrical unit of resistance 1Ω = 1V / 1A Watt (W) Watt is the electrical unit of electric power It measures the rate of consumed energy 1W = 1J / 1s 1W = 1V ⋅ 1A Decibelmilliwatt (dBm) Decibelmilliwatt or dBm is a unit of electric power, measured with logarithmic scale referenced to 1mWOr, the resistance in which one watt of power is dissipated when one ampere flows through it

Introduction To Circuits And Ohm S Law Video Khan Academy
ω meaning in electricity
ω meaning in electricity-Poles lie at a distance ωn from the origin, and at an angle ±cos−1(ζ) from the negative real axis The poles for an underdamped secondorder system therefore lie on a semicircle with a radius defined by ω n , at an angle defined by the value of the damping ratio ζSI Derived Units / Abgeleitete SIEinheiten English / German Frequency / Frequenz hertz Hz = 1/s Force / Kraft newton N = m kg/s 2 Pressure, stress / Druck, mechanische Spannung pascal Pa = N/m 2 = kg/m s 2 Energy, work, quantity of heat / Energie, Arbeit, Wärmemenge joule J = N m = m 2 kg/s 2 Power, radiant flux / Leistung watt W = J/s = m 2 kg/s 3 Quantity of electricity, electric



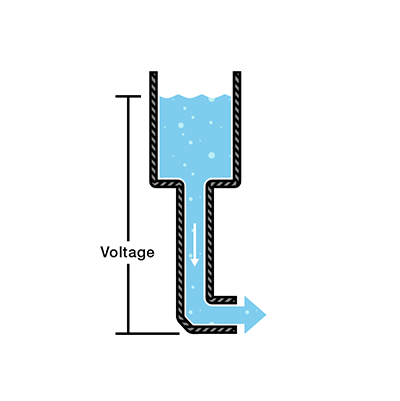
Understanding The Basics Of Electricity By Thinking Of It As Water
Therefore, the power consumed by the 2 Ω is 8 W (ii) When 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors are connected in parallel, the voltage across the resistors remains the same Knowing that the voltage across 2 Ω resistor is 4 V, we can calculate the power consumed by the resistor as follows The power consumed by the 2 Ω resistor is 8 W 15 The list of abbreviations used in a set of engineering drawings varies from office to office Be sure to check the front section of the drawing set for the abbreviations used within that particular set of drawingsA 040 kJ b 019 kJ
Calculate the standing wave ratio on a 50Ω transmission line connected to the dipole antenna Solution According to Eq (948), a half wave dipole has a radiation resistance of 73 Ω To the transmission line, this behaves as a load, so the reflection coefficient is Γ Rrad Z0 Rrad a Z0 73 Ω 50 Ω 73 Ω 50 Ω 0 187 nd th e sa ig w v r o SOhm's Law Calculator – Power, Current, Voltage & Resistance Calculator Below are the four Electrical calculators based on Ohm's Law with Electrical Formulas and Equations of Power, Current, Voltage and Resistance in AC and DC Single phase & Three Phase circuit Enter the known values and select a conversion from the buttons below and click on Calculate result will display Ohm's Law Definition Ohm's Law states that electric current is proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance;
Translingual ·The symbol for ohm, the unit of electrical resistance in the International System of Units··The upper case letter omega (ωμέγα), the last letter of the modern Greek alphabet The upper case letter omega (Ω) is used as the mathematical notation or symbol for the last place in a set or group of itemsAncient Greek ὦ, later ὦ μέγα, Modern Greek ωμέγα) is the 24th and final letter in the Greek alphabetIn the Greek numeric system/Isopsephy (), it has a value of 800The word literally means "great O" (ō mega, mega meaning "great"), as opposed to Ο ο omicron, which means "little OIn electrical terms, this is represented by two circuits with equal voltages and different resistances The circuit with the higher resistance will allow less charge to flow, meaning the circuit with higher resistance has less current flowing through it This brings us back to Georg Ohm Ohm defines the unit of resistance of "1 Ohm" as the




Electrical Units And Metric Prefixes Examples




Ohm S Law Definition Relationship Between Voltage Current Resistance Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
In physics, Ω represents the ohm, a unit of electrical resistance It is the logo of the Omega watch firm The letter omega is the twentyfourth and last letter found in the Greek alphabet and has symbols for both upper and lower case, these are Ω and ω respectively On the other hand, in ancient Greece, it is written as Ωμέγα Questions NCERT Question 7 The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below – I (amperes) 05 10 30 40 V (volts) 16 34 67 102 132 Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor View Answer NCERT Question 8 The values of current I flowing in aFind out what is the full meaning of Ω on Abbreviationscom!



Physics Tutorial Ohm S Law And The V I R Relationship




What Is Ohms Law Formula Equation Electronics Notes
Ohm, abbreviation Ω, unit of electrical resistance in the metrekilogramsecond system, named in honour of the 19thcentury German physicist Georg Simon OhmIt is equal to the resistance of a circuit in which a potential difference of one volt produces a current of one ampere (1Ω = 1 V/A);Electric power definition The electric power P is equal to the energy consumption E divided by the consumption time t P is the electric power in watt (W) E is the energy consumption in joule (J) t is the time in seconds (s) Example Find the electric power of an electrical circuit that consumes 1 joules for secondsIn physics, angular frequency ω (also referred to by the terms angular speed, radial frequency, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rateIt refers to the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as




Introduction To Circuits And Ohm S Law Video Khan Academy




Electrical Resistance What Is It Symbol Formula Ac Vs Dc Resistance Electrical4u
Indicate that each turn around the spiral represents an integer power of ω it represents the space of the differential forms For example, "A differential kform ω is called closed if its outer differential is zero, that is, dω = 0" In telecommunications, it is related to the spectrum of the continuous signalResistances range over many orders of magnitude Some ceramic insulators, such as those used to support power lines, have resistances of 10 12 Ω or more A dry person may have a handtofoot resistance of 10 5 Ω, whereas the resistance of the human heart is about 10 3 Ω A meterlong piece of largediameter copper wire may have a resistance of 10 −5 Ω, and superconductors have noRS – Chapter 1 – Random Variables 4 Definition The σalgebra generated by Ω, denoted Σ, is the collection of possible events from the experiment at hand Example We have an experiment with Ω= {1, 2}




Ohm S Law Definition History Formula Faq Sitename




W Wiktionary
Omega denoted as Ω (in uppercase) and ω (in lowercase) is the last (and 24 th) letter of the Greek alphabet In modern Greek, the Omega letter is transcribed simply as o or ō It also represents the value of 800 in the Greek numeric system, whichElectricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric chargeElectricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equationsVarious common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating,Looking for the definition of Ω?



Resistance Teaching Advanced Physics




In An Electrical Circuit Two Resistors Of 2 Omega And 4 Omega Respectively Are Connected In Youtube
What is electrical current?Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substationThe interconnected lines which facilitate this movement are known as a transmission networkThis is distinct from the local wiring between highvoltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distributionThe resistance R in ohms (Ω) is equal to the squared voltage V in volts (V) divided by the power P in watts (W) The resistance R in ohms (Ω) is equal to the power P in watts (W) divided by the squared current I in amps (A) Amps calculations The current I in amps (A) is equal to the voltage V in volts (V) divided by the resistance R in ohms




Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com



3
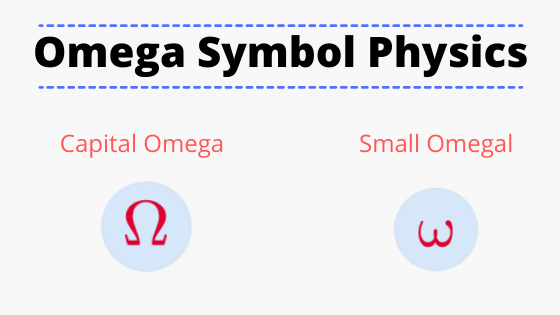
Resistance (also known as ohmic resistance or electrical resistance) is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit Resistance is measured in ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω) The larger resistance, the greater the barrier against the flow of current When the potential difference is applied to a ω = 2π f (rad/s) As the frequency of AC current in India is 50 Hz, the angular velocity can be measured as rad / sec Angular velocity is defined as the velocity of the circular motion of the coil in AC current generator As we already explained above, it is denoted by ωDIRECT CURRENT or DC is similar to the normal flow of water in a hose – it flows in one direction, from the source to the end Historically, DC was originally championed by Thomas Edison in the famous Current Wars of the late 1800s DC lost the war for the grid but it




Omega Symbol Sign And It S Meaning Greek Alphabet W W Ohm Symbol



Ohm S Law Calculation Calculator Calculate Power Formulas Mathematical Ohm S Law Pie Chart Electric Voltage Drop Electric Current Resistance Formula Watt S Law Emf Magic Triangle Equation Tip Online Voltage Volts Resitor Resistance Amps
Ohm (Ω) Ohm (symbol Ω) is the electrical unit of resistance The Ohm unit was named after George Simon Ohm 1Ω = 1V / 1A = 1J ⋅ 1s / 1C 2 Table of resistance values of Ohm ELECTRICITY ELECTRIC CURRENT If the electric charge flows through a conductor (for example, through a metallic wire), we say that there is an electric current in the conductor Definition Electric current is defined as the rate of flow of charge flowing through a crosssection of a wire/conductor Formula If a net charge Q, flows across any crosssection of a17 What electric field is necessary to drive a 75A current through a silver wire 095 mm in diameter?



Omega Symbol Physics Uppercase And Lowercase Omega Symbol Meaning




Ohm S Law Explained Voltage Current Resistance Power Volts Amps Watts Basic Electricity Youtube
Omega / ˈ oʊ m ɪ ɡ ə, oʊ ˈ m ɛ ɡ ə, oʊ ˈ m eɪ ɡ ə / (capital Ω, lowercase ω;Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions Understanding electricity requires knowledge of these basic electrical terms Alternating Current (AC) — An electric current that reverses its direction many times a second at regular intervals Ammeter — An instrument for measuring the flow of electrical current in amperesResistance definition Resistance is an electrical quantity that measures how the device or material reduces the electric current flow through it The resistance is measured in units of ohms (Ω) If we make an analogy to water flow in pipes, the resistance is bigger when the pipe is thinner, so the water flow is decreased



Definition Of Ohm S Law Explanation Measurement Of Electrical Resistance




Omega Symbol Sign And It S Meaning Greek Alphabet W W Ohm Symbol
Solution From Ohm's law (which applies to silver) and the definition of current density (which we assume is uniform in the wire) one finds E = ρJ = ρI=1 4 πd2 = (159 × 10−81 4 π(095 mm)2 = 0168 V/m Problem 19Ohm's Law is Named after the Great German Physicist and Mathematician – Georg'angular velocity' is one option get in to view more @ The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resource




Calculating Omega W In A Separately Excited Dc Motor Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg
How to convert Ohm to Milliohm (Ω to mΩ)?Omega The 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet Commonly used to make things sound mysteriously powerful and amazing The symbol can be created by holding the ALT key and pressing 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, and 0 on the number pad Contrast alpha A free online environment where users can create, edit, and share electrical schematics, or convert between popular file formats like Eagle, Altium, and OrCAD Transform your product pages with embeddable schematic, simulation, and 3D content modules while providing interactive user experiences for your customers




Ohm S Law Definition Formula Applications Of Ohm S Law Videos




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg
Find out in this video!Next video on voltage http//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=TBtkxYfyncWebsite http//wwwafroteThe rms power (as defined here) has no obvious useful meaning (no obvious physical/electrical significance), other than being a quantity that can be calculated as an exercise It is a trivial exercise to perform the same analysis using a 1 A rms sinusoidal current through a 1 Ω resistor Electricity 1 – DC, AC, Batteries, and Transformers How does electricity work in electronics and the grid?




Ohms Law For Dummies 5 Steps Instructables



Electrical Units And Metric Prefixes Examples
Reactive Power — Reactive power is the portion of electricity that establishes and sustains the electric and magnetic fields of AC equipment Exists in an AC circuit when the current and voltage are not in phase Measured in VARS Resistance (Ω Ohms) — The opposition to the passage of an electric current Electrical resistance can beHow voltage, current, and resistance relate An electric circuit is formed when a conductive path is created to allow free electrons to continuously move This continuous movement of free electrons through the conductors of a circuit is called a current, and it is often referred to in terms of "flow," just like the flow of a liquid through a hollow pipeThe equivalent resistance for three resistors in series is 10 Ω15 Ω Ω=45Ω Power P=I2R=05*45=225W 10 A 10V battery is connected to a 15Ω resistor and an unknown resistor R, as shown The current in the circuit is 040 A How much heat is produced in the 15Ω resistor in min?



Resistance Ohm S Law What Is Electrical Resistance Tecnologia Eso En Ingles
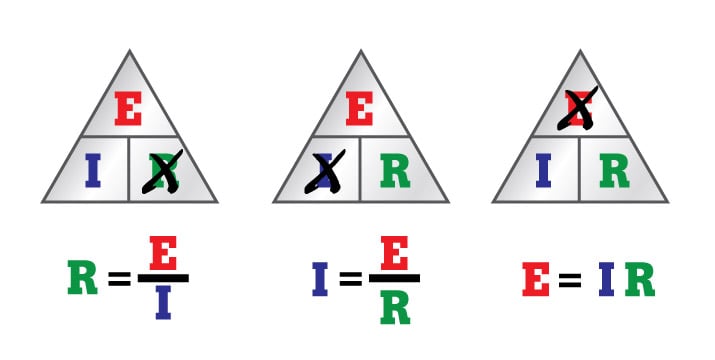



What Is Ohm S Law Fluke
Find the power dissipated in a 25Ω electric heater connected to a 1V outlet Solution Chapter 21 Electric Current and DirectCurrent Circuits Q30P The current in a 1V reading lamp is 26 A If the cost of electrical energy is $0075 per kilowatthour, how much does it cost to operate the light for SolutionRounding errors may occur Definition In relation to the base unit of electric resistance => (ohm), 1 Ohm (Ω) is equal to 1 ohm, while 1 Milliohm (mΩ) = 0001 ohm 1 Ohm to common electricresistance unitsHow to convert Megaohm to Ohm (MΩ to Ω)?
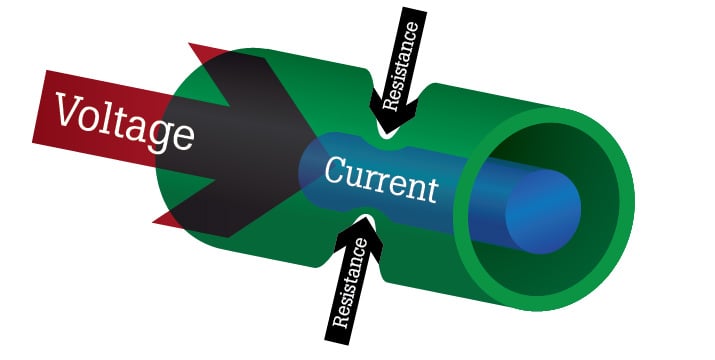



What Is Resistance Fluke




3 Ways To Read A Digital Ohm Meter Wikihow
Who Invented Ohm's Law?1 Ω = 1000 mΩ 1 x 1000 mΩ = 1000 Milliohm Always check the results;Load = Output power as a % of rated power I = RMS current, mean of 3 phases I r = Nameplate rated current V = RMS voltage, mean linetoline of 3 phases V r = Nameplate rated voltage Load = I I r x 100% V V r x Table 1 Induction Motor Synchronous Speeds Poles 60 Hertz 2 3600 4 1800 6 10 8 900 10 7 12 600 6 100% t FullLo 50% Slip 0% 0% No
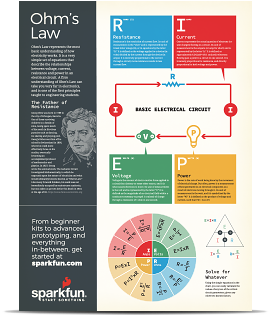



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com
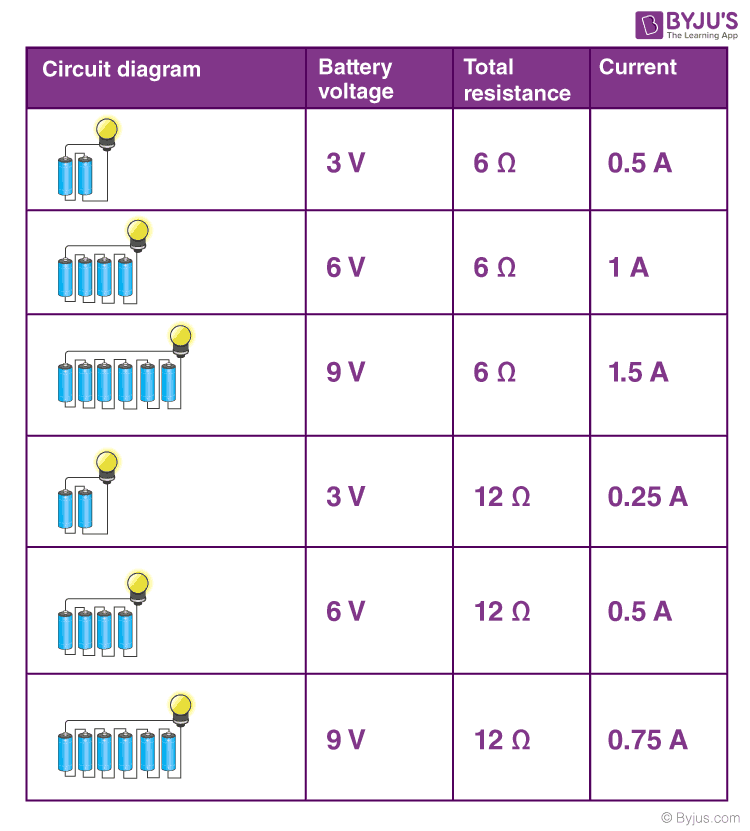



Ohm S Law Statement Formula Solved Examples Verification Faqs
Mathematically, the law states that V = IR, where V is the voltage difference, I is the current in amperes, and R is the resistance in ohms;Answer (1 of 7) Basically it is the root of x^2x1=0 \omega=\frac{1\pm \sqrt{1^24}}{2}=\frac{1\pm \sqrt{3}}{2}=\frac{1\pm i\sqrt{3}}{2} Now why this only It Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit Resistance is measured in ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω) Ohms are named after Georg Simon Ohm (), a German physicist who studied the relationship between voltage, current and resistance He is credited for formulating Ohm's Law




11 2 Ohm S Law Electric Circuits Siyavula



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com
1 MΩ = Ω 1 x Ω = Ohm Always check the results;Rounding errors may occur Definition In relation to the base unit of electric resistance => (ohm), 1 Megaohm (MΩ) is equal to ohm, while 1 Ohm (Ω) = 1 ohm 1 Megaohm Electrical energy is a form of energy resulting from the flow of electric charge Energy is the ability to do work or apply force to move an object In the case of electrical energy, the force is electrical attraction or repulsion between charged particles Electrical energy may be either potential energy or kinetic energy, but it's usually




Resistance And Resistors Boundless Physics



Ohm S Law




Resistance




Inside Meow Wolf S New Omega Mart In Las Vegas The Hollywood Reporter




Voltage What Is It Definition Formula And How To Measure Potential Difference Electrical4u




Omega Symbol Sign And It S Meaning Greek Alphabet W W Ohm Symbol




Ohm S Law The Engineering Mindset




Resistance Electronics Britannica



Law Of Large Numbers Libres Pensees D Un Mathematicien Ordinaire
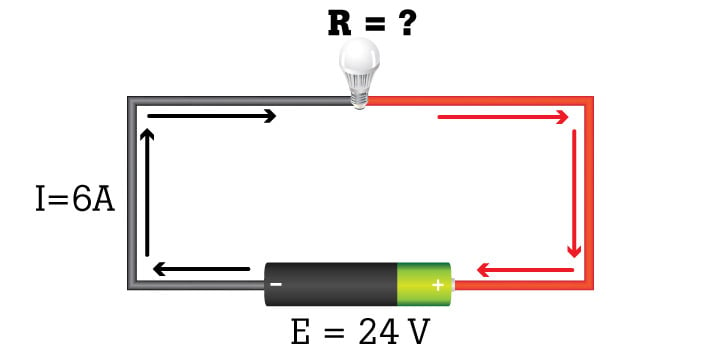



What Is Ohm S Law Fluke



Electrical Resistance The Electricity Forum
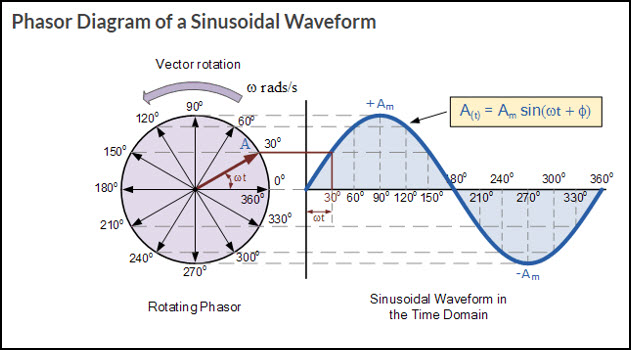



Relation Of Radians Angular Velocity To Ac Gbc Electronics Technician



What Does Volts Amps Ohms And Watts Mean



Understanding The Basics Of Electricity By Thinking Of It As Water




How Voltage Current And Resistance Relate Ohm S Law




Ohm S Law Flashcards Quizlet
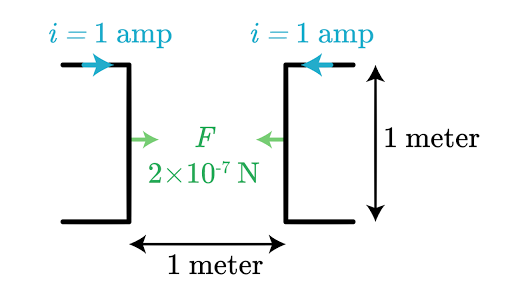



Defining The Standard Electrical Units Article Khan Academy




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg




Ohm S Law With Simple Explanation Examples



Understanding Ohm S Law Impedance And Electrical Phase 101 Audioholics




Ohm S Law Definition Formula Example Voltage Current And Resistance




Ohm S Law Definition Formula Applications Of Ohm S Law Videos




3 Ways To Read A Digital Ohm Meter Wikihow




Ohm Wikipedia




Ohm Wikipedia




Omega Symbol W W Definition In Word Excel Alt Code Mac



1



Episode 108 Resistance Iopspark




Ohms Law An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Ohm S Law



Ohm S Law Power And Energy Circuit Basics
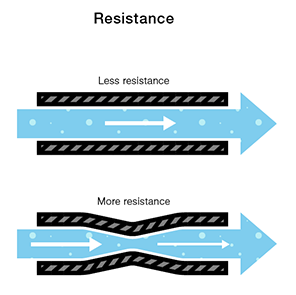



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com
/electrical-conductivity-in-metals-2340117-finalv2-ct-e968693d8c4a4a4ab44de2df68602888.gif)



Electrical Conductivity Of Metals




Ohms Law Png Images Pngwing




Resistors And Ohm S Law Ppt Download
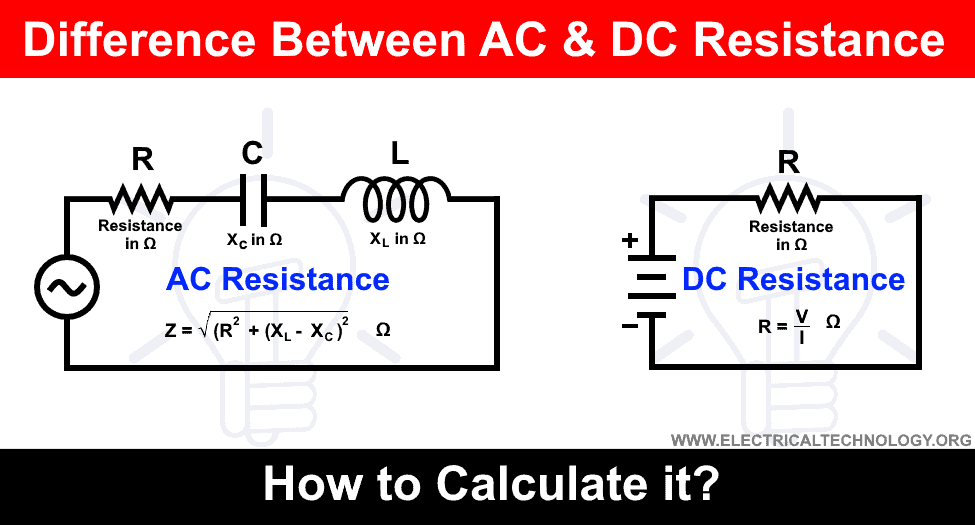



Difference Between Ac And Dc Resistance Which One Is More
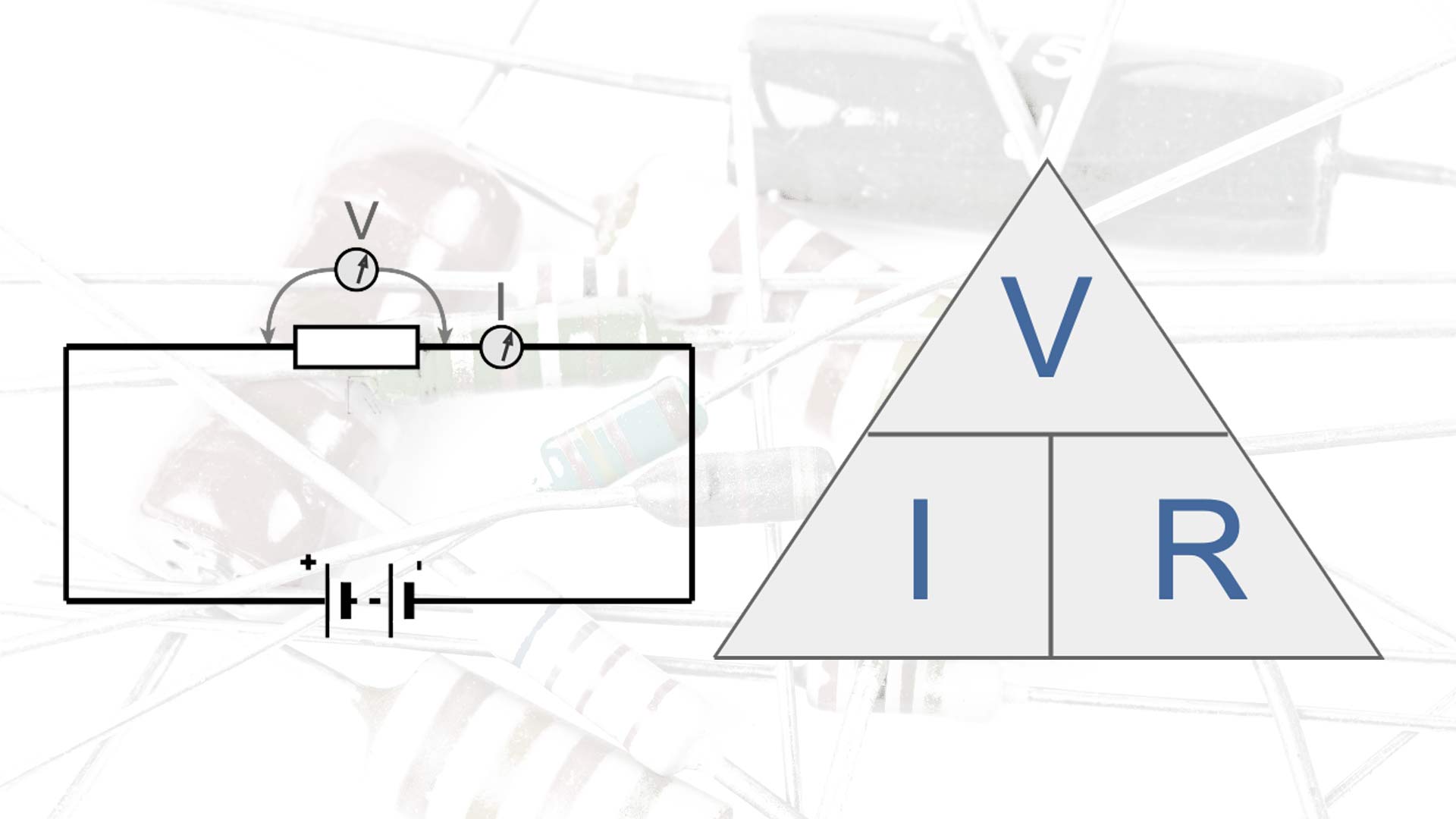



What Is Ohms Law Formula Equation Electronics Notes



Ohm S Law Definition Formula Example Voltage Current And Resistance




Ohm S Law Of Current Electricity Definition Limitations Videos Examples




Electricity Is Not Sorcery Isd Software Solutions
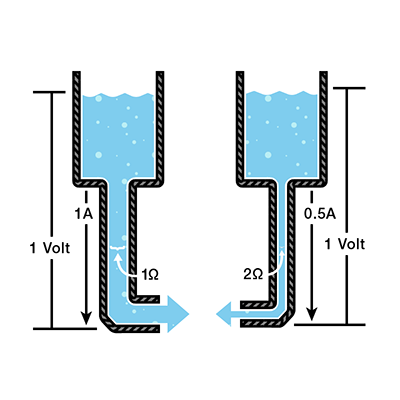



Voltage Current Resistance And Ohm S Law Learn Sparkfun Com



Electric Current Ohm S Law



How To Understand Electricity Watts Amps Volts And Ohms Owlcation



Ohm S Law For Beginners And Novices




Basic Electricity Resistance And Ohm S Law Youtube




Getting Started With Your Multimeter Make




Ohm S Law Symbol Voltage Omega Peace Symbol Text Electrical Wires Cable Png Pngegg
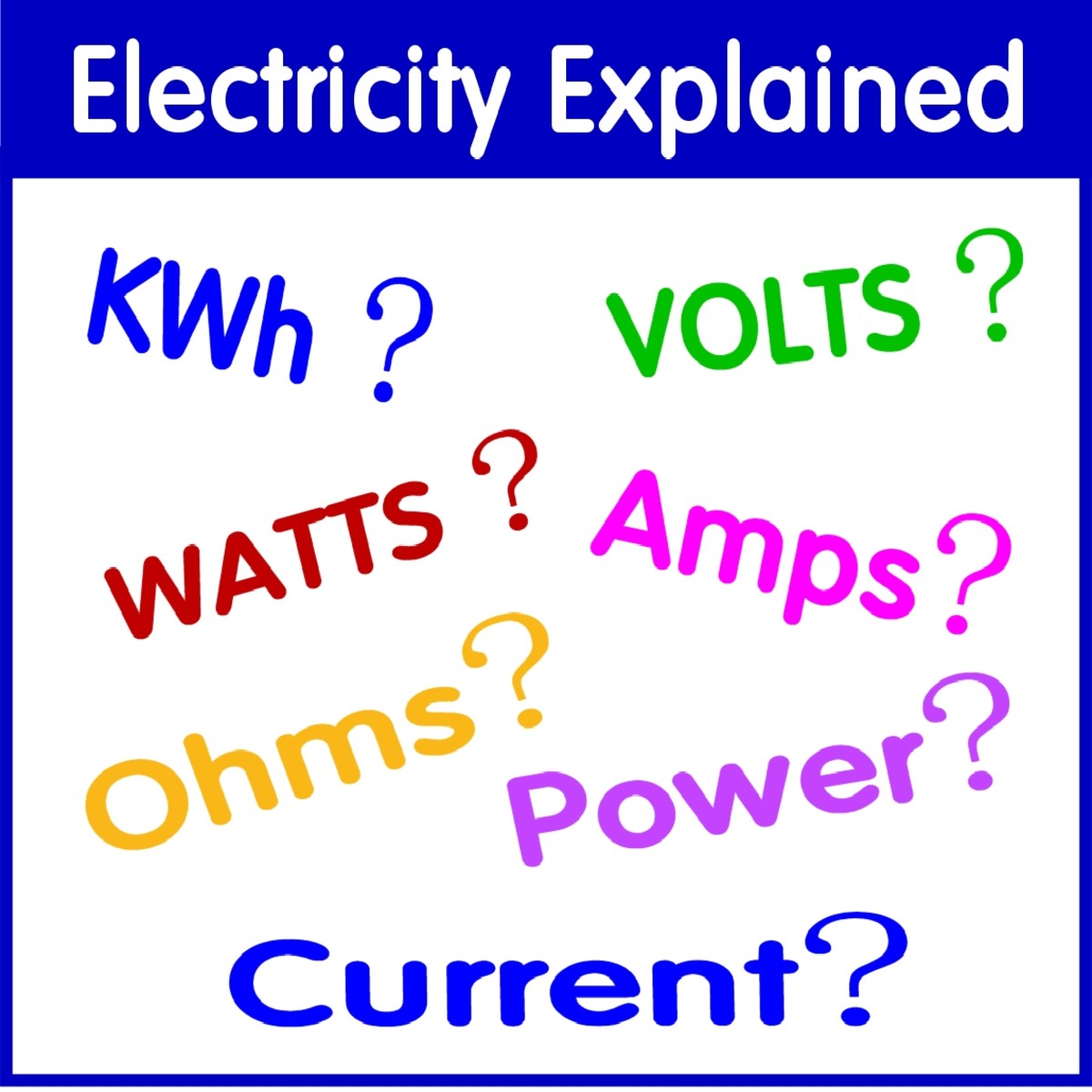



How To Understand Electricity Volts Amps Watts And Electrical Appliances Dengarden



1




Ohm S Law Essential Learning For Electricians



Electrical Formulas




Ohm S Law Definition Formula Applications Of Ohm S Law Videos
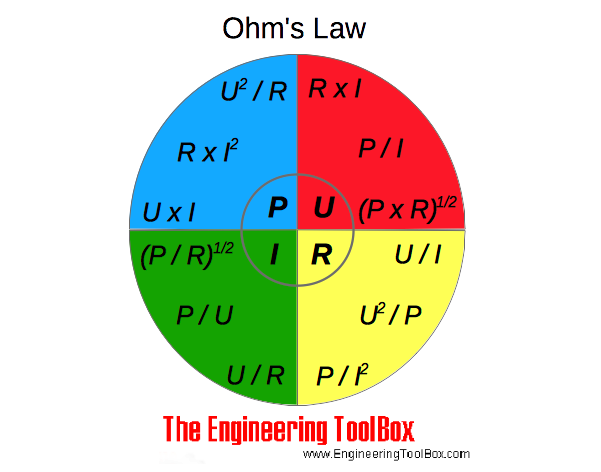



Ohm S Law



Chapter 3 Basic Electronics



1




Q It E Qv Calculations Ohm S Law V Ir Investigating Factors Affecting Resistance I V Graph Characteristics Diode Ohmic Conductor Filament Lamp Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
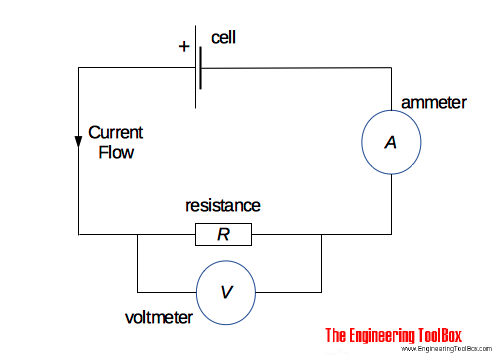



Electrical Units
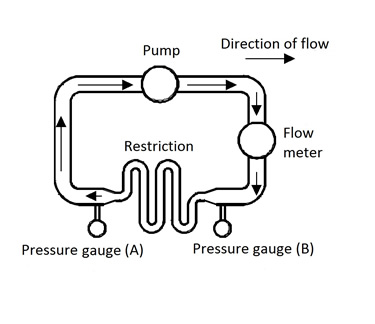



Current Voltage And Resistance Humane Slaughter Association




Omega Symbol W W Meaning Alt Codes How To Write In All Devices



What Does W Stand For In Physic And Also Name The Symbol Quora
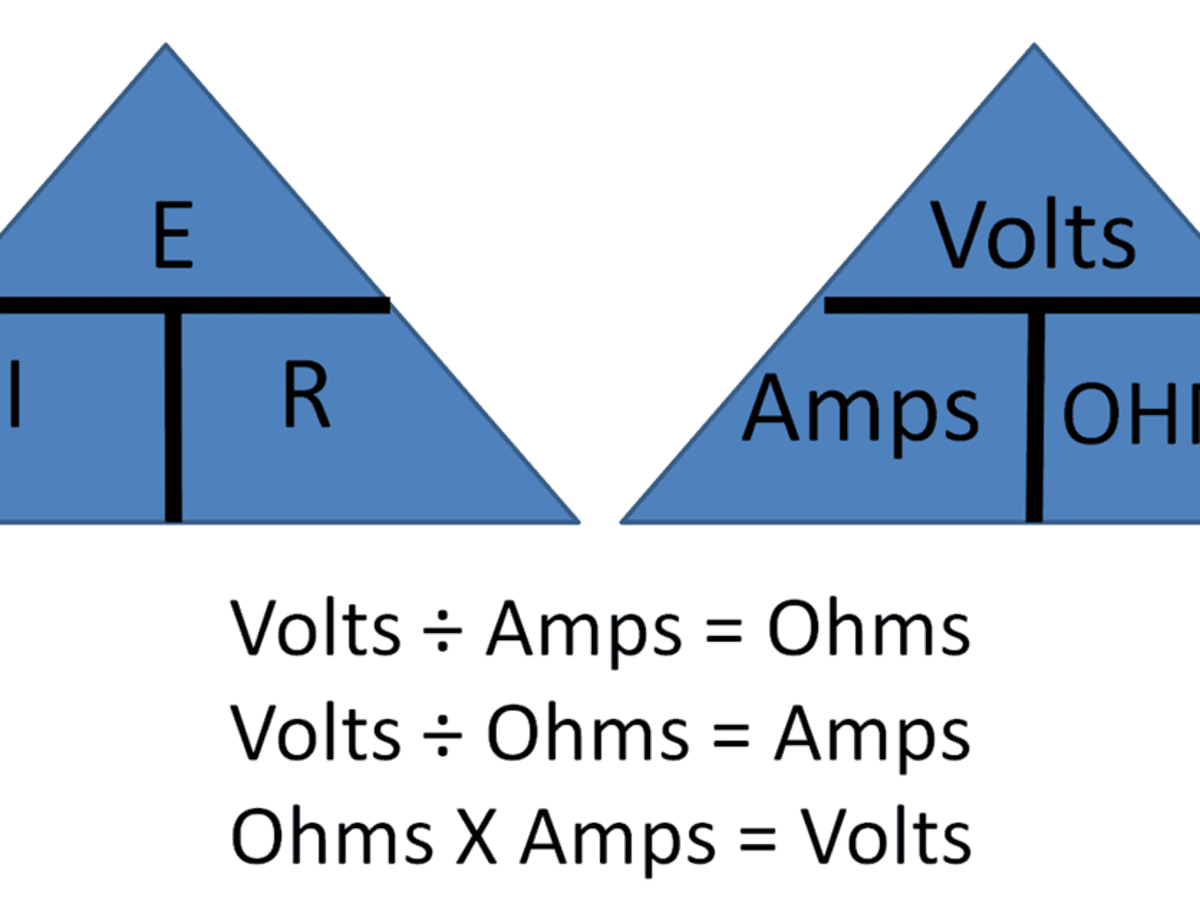



Using Ohm S Law In Basic Electrical And Electronics Testing In Vehicles Axleaddict




Electricity Alternating Current Circuits Britannica




Ohm S Law Wikipedia
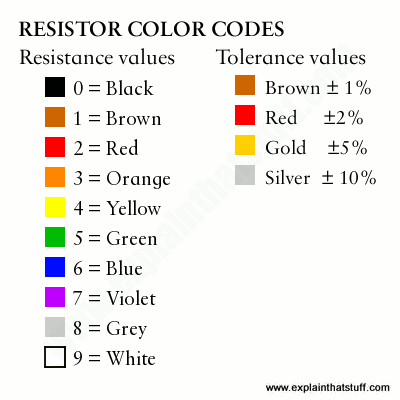



How Do Resistors Work What S Inside A Resistor
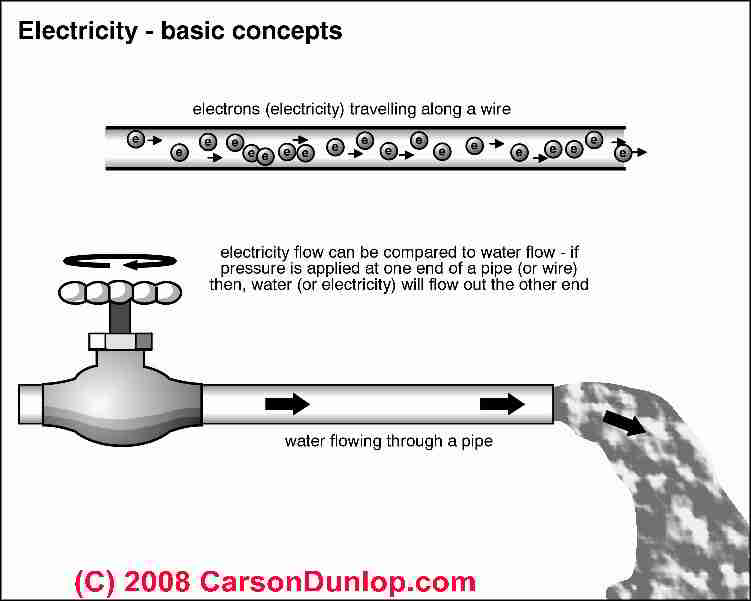



Definition Of Ohm S Law Explanation Measurement Of Electrical Resistance
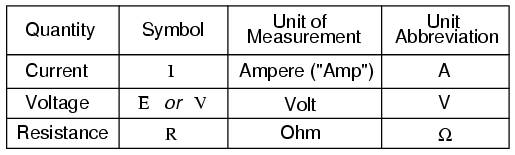



Ohm S Law How Voltage Current And Resistance Relate Ohm S Law Electronics Textbook




What Is Ohm S Law A Simple Explanation Electrical4u
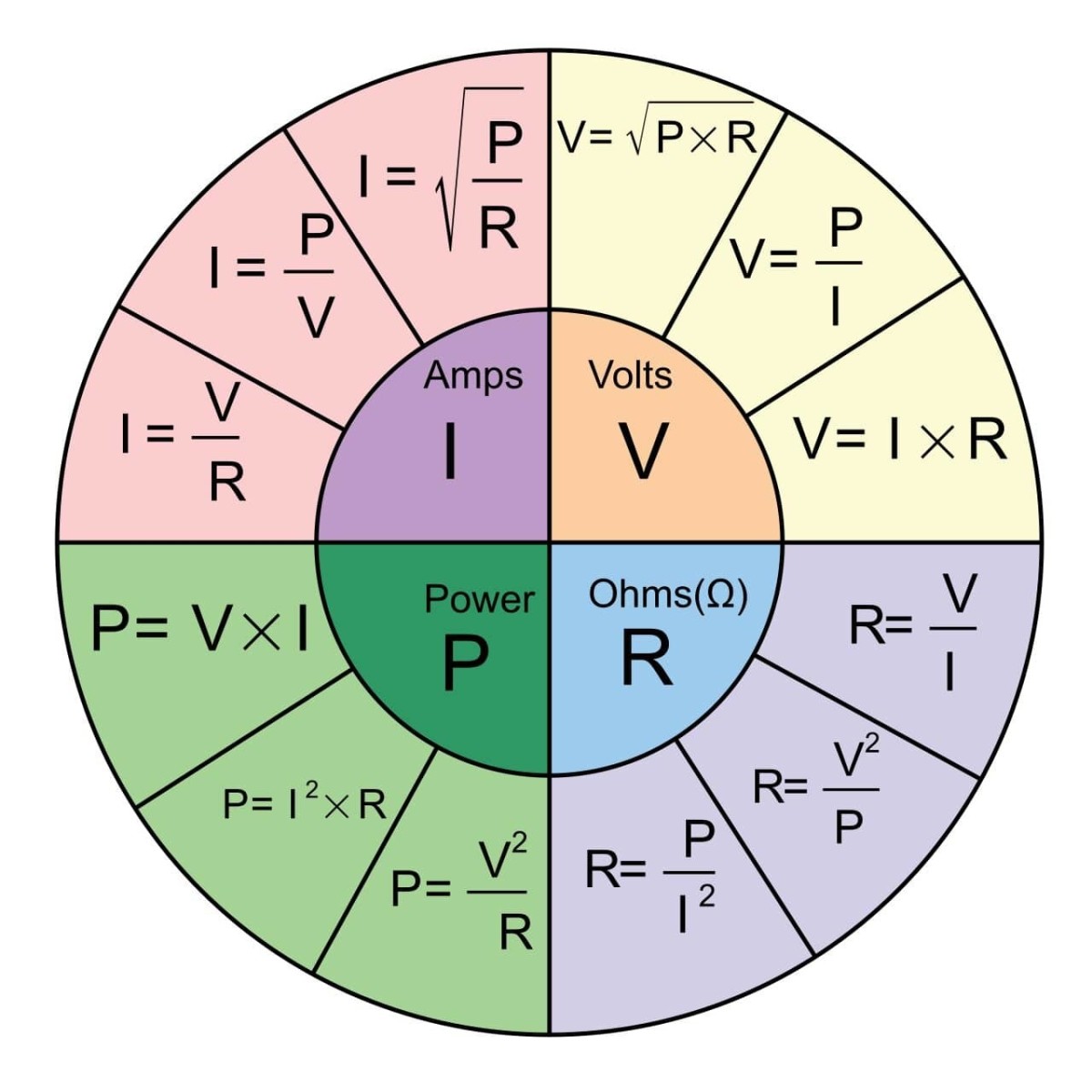



How To Understand Electricity Volts Amps Watts And Electrical Appliances Dengarden




Omega Symbol W W Definition In Word Excel Alt Code Mac




What Is Ohm S Law And How Does It Apply To Thermal Systems Watlow



Electrical Resistance The Electricity Forum




How To Understand Electricity Watts Amps Volts And Ohms Owlcation



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿